'Google Chrome 138' stable release, release of API that provides text summarization and translation functions

The latest stable version of the web browser ' Google Chrome ', version 138, has been released. It has released an API that uses language models to summarize and translate text, significantly reducing the effort required for web developers to implement language model functions. It also includes a number of updates to reduce security risks.
Chrome 138 | Release notes | Chrome for Developers
◆Summarizer API
The Summarizer API is a JavaScript API that summarizes input text based on an AI language model. Until now, to implement a similar function, websites had to either prepare their own language models of several GB in size or send the input text one by one to a third-party web API. The Summarizer API uses the language model built into the browser, eliminating the need for such cumbersome implementation.

You can check the operation of this API on the following demo site.
Summarization API Playground
◆Language Detector API
The Language Detector API is a JavaScript API that detects the language of input text with confidence. Language detection plays an important role in supporting translation, for example when an unknown language is input and it needs to be translated into a specific language. Browsers already have language detection functionality built in, and providing a JavaScript API as a gateway to this functionality allows web developers to use it.

◆Translator API
The Translator API is a JavaScript API that provides language translation capabilities for web pages. While browsers are increasingly providing language translation for users, there are still cases where the browser's built-in translation capabilities cannot handle content that is not part of the DOM (such as translating user input or other interactive features, or voice content), so developers have had to call cloud APIs or implement technologies such as WebAssembly or WebGPU to run their own translation models. For these cases, the Translator API provides language translation capabilities to web developers.

◆ Escaping '<' and '>' in attribute values
The HTML specification has been updated to escape '<' and '>' in attribute values when
Typically, HTML sanitizers are used as follows, where a markup string is first serialized and then reparsed:

Now, consider the following example of a specific markup string:

If we parse this into a DOM tree, we get the following structure:
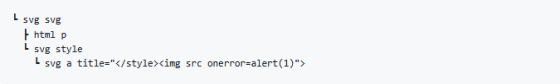
By itself, this markup string does not appear to be particularly dangerous, so it is serialized as follows:

If you reparse the serialized markup string, it will be interpreted as the following DOM tree. What is noteworthy here is that an img tag has appeared, even though it did not exist when parsed before serialization.

To prevent this from happening, you need to escape '<' and '>' when serializing.

Please note that this specification change is a 'breaking change' that does not guarantee backward compatibility, and its impact is described in detail below.
HTML Specification Change: Escaping < and > in Attributes | Blog | Chrome for Developers
◆ Provide OS-level font scale as a CSS environment variable
Until now, there was no way to effectively reflect the font size settings that users have made at the OS level on web pages. Therefore, the OS-level font scale can now be used in CSS as the preferred-text-scale environment variable. For example, if text size is set to double by 'text-size-adjust:auto', the return value of env(preferred-text-scale) will be 2.
◆CSS sibling-index()・sibling-count()
Both sibling-index() and sibling-count() are functions that can be used as CSS property values, allowing you to style an element based on its position or total number of siblings. These functions can be used directly as integer values, but they are more expressive when used inside calc() expressions.

◆CSS size setting keyword: stretch
Stretch is a keyword that can be used as a value for CSS sizing properties (such as width and height). When used, it expands the size of the specified element until it completely fills the available space of the parent block. The difference between stretch and specifying 100% is that the size obtained by specifying it is the size of the margin block of the parent element, not the box specified by box-sizing. In other words, by using this keyword, you can make the element as large as possible while maintaining the margins of the parent element.
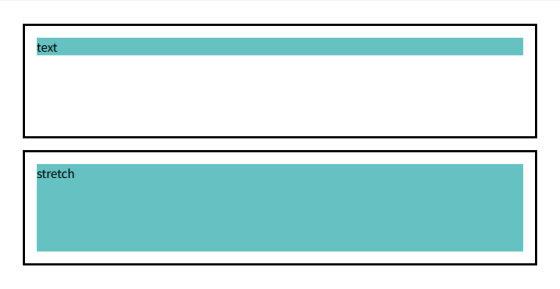
As an example, let's look at the following HTML:

Of the two areas consisting of parent and child elements, specify stretch for the height of only one of the child elements.

The results are as shown below. You can see that the side with stretch specified has expanded to the full inside the margin of the parent element.
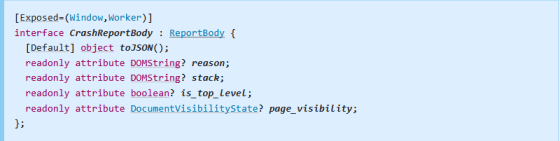
◆Added Crash Reporting fields
is_top_level: A Boolean string indicating whether the document that submitted the crash report belongs to a top-level traversable.
page_visibility: a string indicating whether the viewport was at all visible ('visible') or completely hidden ('hidden').
◆ Script Integrity Policy

* Fixed the return value of StorageManager.estimate()
Sites without unlimited storage permissions will report a predictable storage quota via the StorageManager API. However, because incognito browsing has significantly less storage available than normal browsing, the reported storage quota may allow sites to detect the user's browsing mode. To avoid this, sites with limited storage permissions will now report an artificial quota equal to usage + minimum (10GiB, rounded up to the nearest 1GiB for disk) for all browsing modes. Note that sites with unlimited storage permissions and enforced quotas are not affected by this fix.
◆Other updates
CSS: Sign-related functions abs() and sign()
CSS: Function progress() for interpolation progress
Viewport Segments Enumeration API: Viewport segment management for foldable devices
- WebCodecs: Supports metadata that preserves the orientation of video frames
- Android Web Serial via Bluetooth: Supports serial port connection via Bluetooth
・Prevent HTTP pre-rendering of untrusted plain text: Ensure consistency with pre-fetching
Nested view transitions: Allows you to create hierarchical pseudo element trees
・Pushsubscriptionchange event is issued when resubscribing
Speculation rule: Add prefetchCache and prerenderCache to the Clear-Site-Data header.
Speculation rules: Extend the speculation rules syntax to allow developers to specify the target_hint field.
- Adjusted the semantics of the Storage Access API to strictly comply with the same-origin policy
◆ Deprecated features
- Asynchronous range deletion in Media Source Extensions: Matching the specifications with Safari and Firefox.
Automatic fallback to WebGL with SwiftShader: Reduces security risks
WebGPU's GPUAdapter.isFallbackAdapter boolean attribute
Google Chrome 138 also includes 11 security bug fixes .
The next stable version, Google Chrome 139, is scheduled to be released on Tuesday, August 5, 2025 local time.
Related Posts:
in Software, Posted by log1c_sh