'Google Chrome 137' stable release, introduces if() function to CSS to express conditional values succinctly

The latest stable version of the web browser ' Google Chrome ', version 137, has been released. Many new features have been added, including the introduction of the if() function in CSS, which allows complex conditional logic to be expressed succinctly.
Chrome 137 | Release notes | Chrome for Developers
◆The <use> tag can now reference the root element of an external SVG without specifying a fragment
Previously, when referencing an element within an SVG, it was necessary to specify a fragment (ID).

With this update, if you omit the fragment, it will reference the root element in the SVG.

This is especially useful when you are using an external SVG document and the root element does not have an ID set, as it means you do not have to go through the trouble of editing the SVG document and adding an ID to it.
◆Introducing the if() function to CSS
The introduction of the if() function provides a more concise way of writing CSS conditional values.
Below is an example of a traditional description.

If you were to write the same thing using the if() function, it would look like this:

The if() function takes multiple pairs of 'conditions' and 'values when the conditions are true' separated by semicolons as arguments, and returns the value corresponding to the first condition that is true. In this example, the '--color' CSS custom property is set to white for the dark class and black for the light class, so the foreground color is specified as is, and separate colors are specified for the dark and light classes by using --color as the condition for if() to specify the background color.
Comparing the two statements, the use of if() may at first glance seem more complicated, but the key point is that the entire style is determined by simply deciding on a single value, --color. Also, in the example, a custom property is used directly to specify the color, but if you think of this simply as a conditional value, you can also control various properties other than color collectively with a single custom property, which dramatically increases the concentration of CSS changes that need to be made.
◆Added CSS properties reading-flow and reading-order
The CSS property reading-flow allows you to control the order in which elements in a layout (flex, grid, block, etc.) are focused when using the tab key. Possible values are:
・Normal
・flex-visual
・flex-flow
・grid-rows
・grid-columns
・grid-order
・source-order
On the other hand, the CSS property reading-order allows you to manually override the order in a reading flow container. The value of reading-order is an integer, with a default value of 0.
You can actually see these in action at the following site:
reading-flow examples
https://chrome.dev/reading-flow-examples/
◆Document-Isolation-Policy
The Document-Isolation-Policy can be used by itself to enable crossOriginIsolation without introducing a Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy (COOP) or Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy (COEP) into the document, and regardless of the status of the page's crossOriginIsolation (COI) property.
This makes it possible to safely build fast applications using Shared Array Buffers (SABs) while still maintaining communication with cross-origin popups, and greatly reduces the effort required to embed cross-origin iframes in documents.
Expected use cases include the efficient construction of secure web applications that incorporate convenient features such as oAuth and cross-origin widget embedding while also running computationally intensive tasks (such as video games, video conferencing, and photo editing) with high performance.
◆ Support for signature algorithm Ed25519
The Web Cryptography API now supports Ed25519 as a cryptographic algorithm.
Until now, even though browsers that support TLS 1.3 have Ed25519 built in as a bandwidth transmission algorithm, web developers have not been able to use Ed25519 in their browsers. For this reason, if you want to use Ed25519 in a web application, you have to implement it yourself using JavaScript, WebAssembly, etc. This is not only wasteful and cumbersome, but also has security issues, so API support has been eagerly awaited.
◆Prevent security risks caused by HSTS tracking
We now allow HSTS upgrades only on top-level navigations and block HSTS upgrades on subresource requests, preventing malicious sites from abusing HSTS caches to track your web.
◆ Disable the character spacing setting for cursive writing
The CSS property letter-spacing allows you to specify the space between letters, but when you apply this to cursive text in a language like Arabic, the spaces added can make it difficult to interpret the text as words.
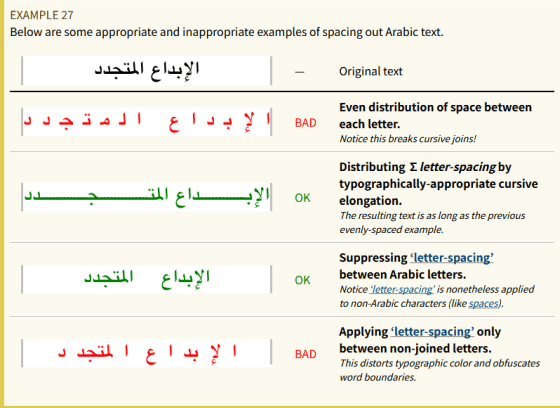
There are two possible solutions to this problem: either stretch or compress the cursive characters instead of adding extra spaces, or not apply the spacing between cursive characters specified by letter-spacing. However, the former requires complex calculations to take into account the unique elements of cursive writing, such as continuity maintenance, stretched glyphs, typeface, and calligraphy, while the latter has the advantage in terms of processing efficiency.
More detailed information on this can be found below:
This support is expected to improve the user experience for speakers of cursive-dependent languages (Arabic, Hanifi Rohingya, Mandaic, Mongolian, Nko, Pags-Pa, and Syriac).
◆ Selection API: getComposedRanges() and direction
The following additions have been made to the Selection API :
・Selection.direction: Indicates the direction of the selection, and can take the values 'none', 'forward', or 'backward'.
Selection.getComposedRanges(): Returns a list of 0 or 1 'composed' StaticRanges.
A normal Range cannot cross the boundary of a shadow root, but a 'composite' StaticRange can.

If the selection range crosses the boundaries of a shadow root not specified in the list, the endpoints of the StaticRange are rescoped to be outside that tree, so that unknown shadow trees are not exposed.
◆ Introducing JavaScript Promise Integration
◆ CSS property 'accent-color'
Using the CSS property accent-color , platform-defined accent colors can now be automatically applied to form elements such as checkboxes, radio buttons, and progress bars. This makes it easier to match the colors used in web applications with the system theme selected by the user, enabling a unified and personalized interface. If no value is specified for accent-color or if it is set to 'auto', the platform standard accent color will be applied.
◆view-transition-name value: match-element
The view-transition-name CSS property has a value of match-element, which is converted to a unique value based on the element's ID. This is intended to be used in single page applications where you want to move an element and animate it with a view transition.
For example, suppose you have a DOM element like this:

Previously, if you wanted to specify a view-transition-name for these, you had to write it like this for each element one by one.

If we rewrite this using match-element, it will look like this:

◆Origin Trial
Added blocking attribute 'full-frame-rate': the renderer will run at a lower frame rate until it has finished parsing the #critical-content element.
- Added permission policy 'media-playback-while-not-rendered': Allows pausing media playback in hidden embedded iframes
Writer API: Generate documents in response to writing task prompts
Rewriter API: Transforms and paraphrases input text in the desired way
◆Other updates
・Change in the exception that occurs when creating WebAuthn authentication information for 'payment' authentication information (SecurityError → NotAllowedError)
・Implemented partitioning for Blob URL access
- Capture JS call stacks when a page becomes unresponsive due to JavaScript code
- Floating-point color values can now be used in the Web API'sCanvasRenderingContext2D , OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D , and ImageData
Improved security monitoring and incident response capabilities through IP address logging and tracking
Language Detector API: A JavaScript API that detects the language of text with confidence.
The offset-path CSS property now supports the shape() function.
SVGSVGElement : Transform properties such as scale, rotation, translation, and skew can be applied directly via the transform attribute on the <svg> root element.
WebAssembly Branch Hints: Improves WebAssembly performance by informing the JavaScript engine that certain branch instructions are highly likely to take certain paths.
- WebGPU: The offset and size parameters of copyBufferToBuffer() are now optional.
- WebGPU: Allows you to use GPUTextureView for external texture binding
Google Chrome 137 also includes 11 security bug fixes .
The next stable version, Google Chrome 138, is scheduled to be released on June 24, 2025 (local time).
Related Posts:
in Software, Posted by log1c_sh







