Individualized instruction using 'AI tutors' improves learning efficiency and increases motivation among university students

When taking difficult lectures at university or elsewhere, some people may have thought, 'I wish there was
AI tutoring outperforms in-class active learning: an RCT introducing a novel research-based design in an authentic educational setting | Scientific Reports
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-97652-6

Professor tailored AI tutor to physics course. Engagement doubled. — Harvard Gazette
https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2024/09/professor-tailored-ai-tutor-to-physics-course-engagement-doubled/
Generative AI, which can converse like humans and has knowledge gained from large datasets, has the potential to significantly advance education, but how effective it will be compared to traditional education is unclear.
So, Gregory Kestin , a physics lecturer at Harvard University, and Kelly Miller, a senior physics lecturer, actually conducted an experiment to examine the effectiveness of 'AI tutors' in a lecture on 'Physical Sciences 2' for students majoring in life sciences at Harvard University.
The experiment took place in the fall of 2023. 194 students who agreed to participate were divided into two groups, each attending lectures for two consecutive weeks. During the first week, one group received active learning from a lecturer in a regular classroom, while the other group received lectures from the 'AI tutor' developed by Kestin and his colleagues at home. During the second week, the two conditions were reversed, and the students attended the lectures again.
The image below shows the screen of the AI tutor used in this study. The AI tutor framework was built on the GPT API provided by OpenAI, and the AI tutor's personality and the quality of its feedback were pre-screened. The AI tutor was given context-rich and sophisticated prompts to answer students' questions. The research team also used their own expertise to create instructions for the AI tutor to follow in each lecture, allowing it to behave like an experienced lecturer.
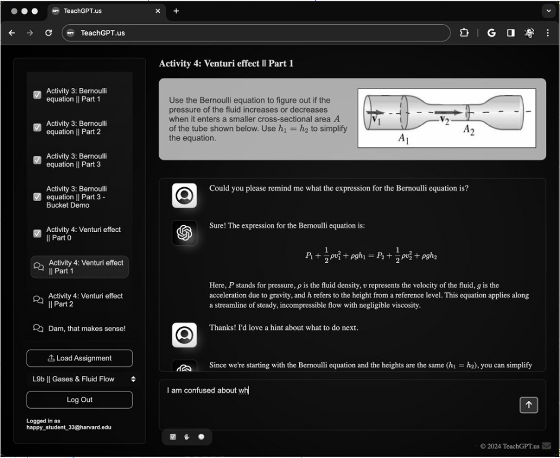
The researchers compared the learning outcomes of each class using pre- and post-tests to measure students' proficiency, and also asked students how engaged they were in each class, how much they enjoyed it, and how motivated they were.
The analysis showed that students who received lectures from AI tutors achieved better learning outcomes than students who received lectures from humans. Students who used AI tutors also reported completing their studies in less time than students who received lectures in a classroom.
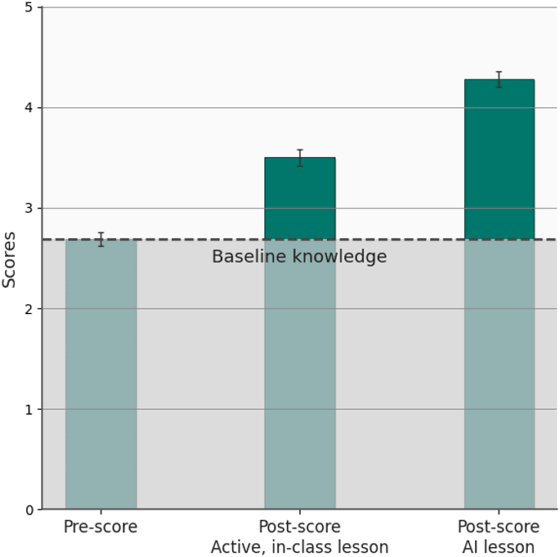
The graph below shows the test scores measured before the lecture (left), the comprehension score after the human lecture (middle), and the comprehension score after the AI tutor lecture (right). Compared to the baseline average score of 2.75, the average score for the human lecture was 3.5, and the average score for the AI tutor lecture was 4.5, resulting in more than twice the learning outcomes for the AI tutor lecture.
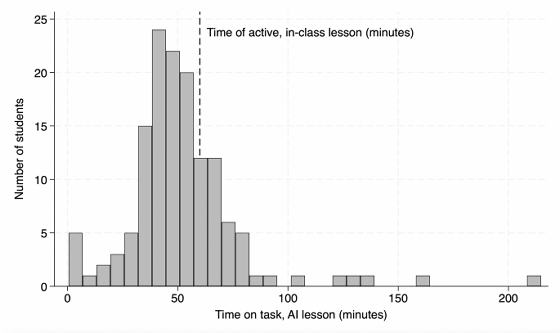
The graph below shows the time spent on tasks by students who received lectures from AI tutors. The dotted line represents the classroom lecture time minus the time for pre- and post-tests (60 minutes). It shows that many students who used AI tutors finished their studies in less than the classroom lecture time. Approximately 70% of students who received lectures from AI tutors finished their studies in less than 60 minutes, with the median time being 49 minutes.
Furthermore, students who received lectures from AI tutors also scored higher on their engagement and motivation than students who received human lectures. 'We never expected that students would find lectures using AI more engaging,' says Kestin.
Miller pointed out that lectures can be boring for students who already have a good knowledge of the material, while those with less knowledge have a hard time keeping up, and argued that AI tutors could help make up for these differences between students.
Based on the results of this study, the research team believes that if AI can be used to teach basic knowledge outside of class hours, valuable class time can be used to teach advanced skills such as 'advanced problem-solving ability, project-based learning, and group work.'
'AI has the potential to dramatically improve learning, but if we're not careful, it could also hinder learning,' Kestin said. 'AI tutors shouldn't 'think' for students, but should help develop critical thinking . AI tutors shouldn't replace face-to-face classes, but should help all students be better prepared.'
Related Posts:
in Software, Web Service, Science, Posted by log1h_ik







