What is the approach needed to accurately detect 'AI that breaks CAPTCHA'?
Proof of Human. Creating the invisible Turing Test for the Internet
https://research.roundtable.ai/proof-of-human/
Google's reCAPTCHA v3 has an overwhelming share of the bot detection market at the time of writing. reCAPTCHA v3 is touted for its ability to analyze users' web behavior patterns, such as mouse movements, input patterns, and browsing history. Nevertheless, reCAPTCHA v3 cannot detect AI agents that use real browser environments.
New bot exclusion tool 'reCAPTCHA v3' has appeared, and by installing it on all pages, it has evolved to the point where no user work is required at all - GIGAZINE

For example, it has been revealed that the AI agent 'Operator ', which can automatically handle complex tasks via OpenAI's browser, can break through the reCAPTCHA v3 authentication test. The following video shows Operator breaking through reCAPTCHA v3.
OpenAI's Operator bypasses Google reCAPTCHA v3 - YouTube
To accurately detect such AI agents, new approaches that focus on behavioral patterns and cognitive characteristics are gaining attention.
What exactly does this behavioral pattern refer to? It refers to the unique patterns of human physical interaction with computers. For example, the dynamics of human typing are irregular and context-dependent. The image below shows a graph of the delays (vertical axis) that occur when a human types a key (horizontal axis). There are some large delays.
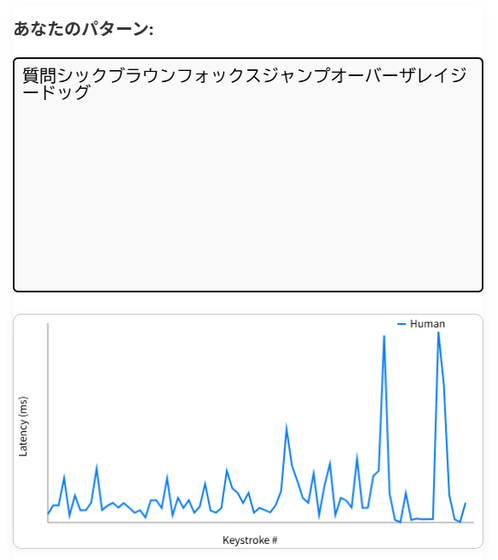
On the other hand, the bot pastes text instantly and 'mimics' human keystrokes with 'unnatural regularity,' so there isn't much delay when typing.
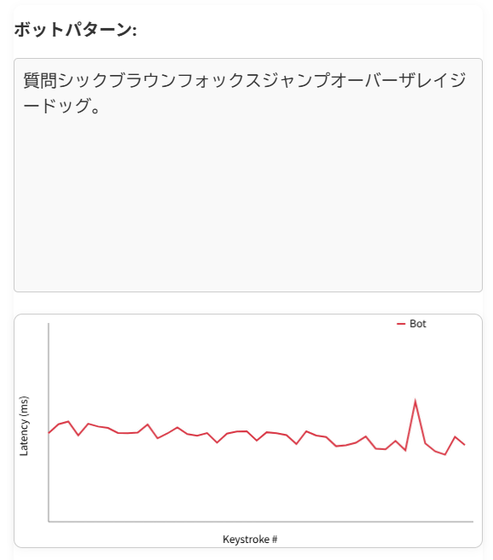
Similarly, human mouse movements have characteristics such as small adjustments and overshooting, whereas bots move the mouse in a straight line or teleport between points. These differences are not only visually obvious, but can also be quantified.
The graph below shows a comparison of the actual mouse movements of a human and a bot. The jitter of the mouse movement is constant for the bot, while it is irregular for the human. The velocity of the mouse also has many moments when the bot is zero, while the human has few moments when the mouse stops completely.
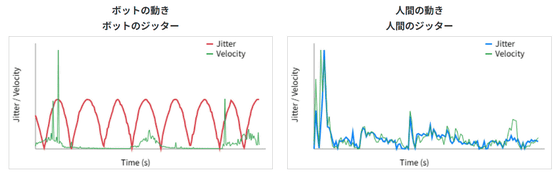
It is unclear how well bots can disguise these behavioral patterns, but previous academic research has shown that behavioral pattern-based authentication is robust against attacks under hostile conditions, and its usefulness has also been demonstrated in industry testing, including by major financial institutions.
The fundamental reason why it is difficult to mimic human behavioral patterns with AI is the cost and complexity. Traditional credentials such as passwords and fingerprints are static, finite, and easily reproducible, whereas behavioral patterns are difficult to reverse engineer. While AI agents could theoretically simulate these patterns, it is clear that the effort required would be greater than other alternatives.
Additionally, there are approaches that focus on cognitive characteristics.
Take the Stroop task , a classic psychological experiment in which humans choose the color a word is written in, rather than the meaning of the word. Humans typically respond slower when the meaning of a word conflicts with its color (e.g. the word 'blue' is written in green). Bots and AI agents, on the other hand, are not subject to such interference and are able to respond at a consistent rate.
Such approaches that apply cognitive characteristics can play an important role in distinguishing humans from AI. If AI is to imitate human cognitive characteristics, it will have to simulate not only the answer to questions but also the human cognitive process, which obviously requires a lot of effort.
Proof-of-Human API is an API for distinguishing humans from AI based on such behavioral patterns and cognitive characteristics. Mayank Agrawal and Mathew Hardy of Roundtable Technologies, the developers of Proof-of-Human API, said, 'We are working on this behavioral and cognitive approach for bot detection and cybersecurity. Rather than focusing on privacy-invasive techniques such as biometric scanning and cookie tracking, we are trying to detect bots by presenting economic challenges to AI agents.'
Roundtable - Invisible bot detection and fraud prevention
https://roundtable.ai/
Related Posts: