It was discovered that Russia was exploiting vulnerabilities in the compression and decompression tool '7-Zip' to attack Ukraine

It has been revealed that the archive creation function of the compression and decompression tool '
CVE-2025-0411: Ukrainian Organizations Targeted in Zero-Day Campaign and Homoglyph Attacks | Trend Micro (US)
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/25/a/cve-2025-0411-ukrainian-organizations-targeted.html
7-Zip 0-day was exploited in Russia's ongoing invasion of Ukraine - Ars Technica
On September 25, 2024, Trend Micro's threat hunting team identified a zero-day vulnerability ' CVE-2025-0411 ' in 7-Zip.
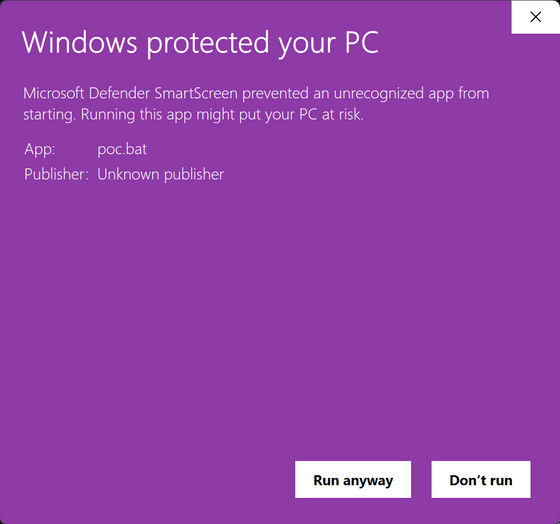
When a user downloads a file from an untrusted source such as the Internet, Windows activates a security feature called Mark-of-the-Web (MoTW). This feature places a 'Zone.Identifier' tag on all downloaded files to allow additional monitoring by Windows Defender SmartScreen and restrictions on how and when the file can be run. If Windows Defender SmartScreen determines that a potentially dangerous application exists, the user will see the following warning:
However, CVE-2025-0411 allows threat actors to defeat MoTW by using 7-Zip's archive creation feature to double archive the contents. In fact, Russian cybercrime groups have been attacking by embedding executable files in an archive and then embedding that archive in another archive.
Trend Micro researcher Peter Jilnas said, 'The root cause of CVE-2025-0411 is that 7-Zip versions prior to 24.09 did not properly apply MoTW protection to the contents of double-encapsulated archives. This allows threat actors to create archives containing malicious scripts or executables that are not subject to MoTW, making Windows users vulnerable to attacks.'
Additionally, to further disguise the attack, the executable file extensions were rendered with so-called '
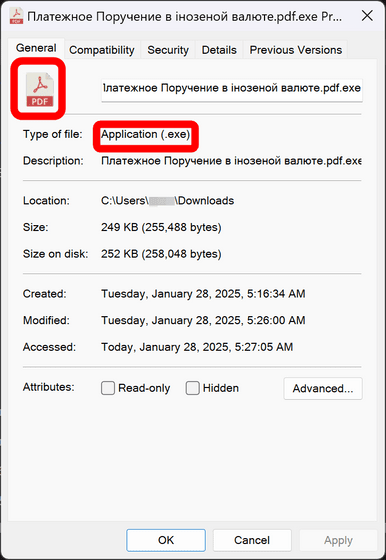
Threat actors who exploited CVE-2025-0411 created an inner archive of document files disguised as '.doc' files using the Cyrillic character 'С'. When opened, JavaScript files (.js), Windows script files (.wsf), and Windows shortcut files (.url) contained within the archive would be executed without MoTW protection. The image below shows an example of a malicious file that appears to be a PDF file at first glance, but actually executes an application (.exe).
Trend Micro's investigation uncovered malicious emails targeting several Ukrainian government agencies, as well as Ukrainian local governments and businesses. The threat actor used a doubly archived file attached to emails to these targets in the attack. Below are the targeted Ukrainian government agencies. Trend Micro stated, 'Those affected by this attack were often small local governments that are not familiar with cybersecurity and lack the resources for a comprehensive cyber strategy that larger government agencies would have.'
・State Executive Service of Ukraine (SES)
- Zaporizhia Automobile Manufacturing Plant (PrJSC ZAZ)
・Kiev Passtran
・SEA Company
Verkhovyna District Administration
・VUSO
Dnipro Regional Pharmacy
・Kiev Vodokanal
- Zalizchiki City Council
In this attack, the threat actor created an inner archive of document files disguised as '.doc' files using the Cyrillic letter 'С', which, when opened, would allow any JavaScript files (.js), Windows Script files (.wsf), and Windows Shortcut files (.url) contained within the archive to run without MoTW protection.
In response to this, Trend Micro conducted an initial analysis and proof of concept, and reported the vulnerability to Igor Pavlov, the developer of 7-Zip, on October 1, 2024. Subsequently, 'Version 24.09 ,' which fixed this vulnerability, was released on November 30, 2024.
Related Posts: